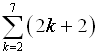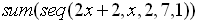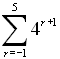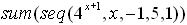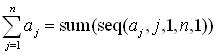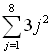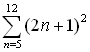|

|
Evaluating Summation Notation
(Function Mode)
|
A shorthand notation is used to represent sums with more than a few
terms. This shorthand notation uses the Greek letter sigma
(which denotes sum). If we have a rule such as f (n)
which assigns the value f (n) to each integer n in the set of integers {j, j+1, j+2, ... k},
we can represent the sum as:
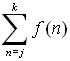 = =
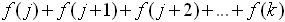
On the graphing calculator:
|
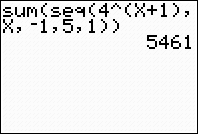
We will be using the sum feature and the seq feature to work with a general
summation.
On the
calculator, we will interpret a summation as follows:
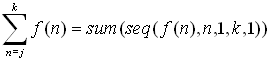
|
|
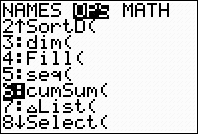
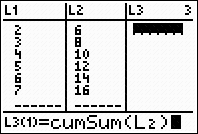
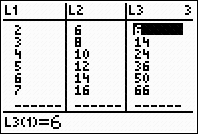
2nd STAT (LIST) → MATH
#5 sum
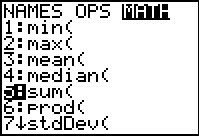
The format for sum is sum( list )
where list will be the terms of
the rule
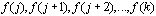 . .
|
2nd STAT (LIST) →
OPS Choose #5 seq(

The format for seq: expression,
variable,
starting value, ending value, increment.
|
|
While sequences have a domain of
natural numbers, {1, 2, 3, 4, ...}, in Func mode, the sequence command will
accept integer domain values less than one. (In Seq mode, however, the sequence command will accept only
integer domain values of 1 or greater.)
|
|
|
|
|
(For ease of entry, X was used as the variable in both examples above.
If you wish to use the designated variable, type it into the
calculator using the alpha
key.)
|
| Summations and Sequences: |
Sums, such as 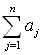 ,
where j = 1, may represent the summation of a sequence, called
a series. ,
where j = 1, may represent the summation of a sequence, called
a series.
 |
Remember, sequences have a domain
of natural numbers, {1, 2, 3, 4, ...}.
In the sequence related
problems below, the starting
value in the summation will be greater than or equal to 1.
|
Again, we will be using the sum and seq features of the calculator to find the summations. The
summation is interpreted as:
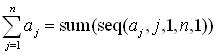
|
|
2nd STAT (LIST) → MATH
#5 sum
 |
2nd STAT (LIST) →
OPS Choose #5 seq(
 |
|
|
|
| Example 3:
Evaluate: 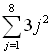
|
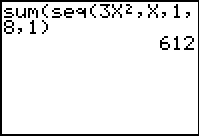
This example uses x as the variable,
instead of using j. The x is simply
easier to enter into the calculator.
|
| Example
4:
Evaluate: 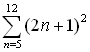 |
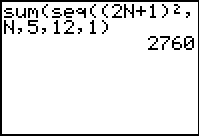
This example uses n as the variable -- obtained by engaging the
alpha key.
|

Finding Your Way Around TABLE of
CONTENTS
|
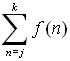 =
=
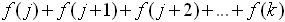

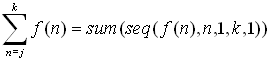

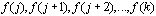 .
.